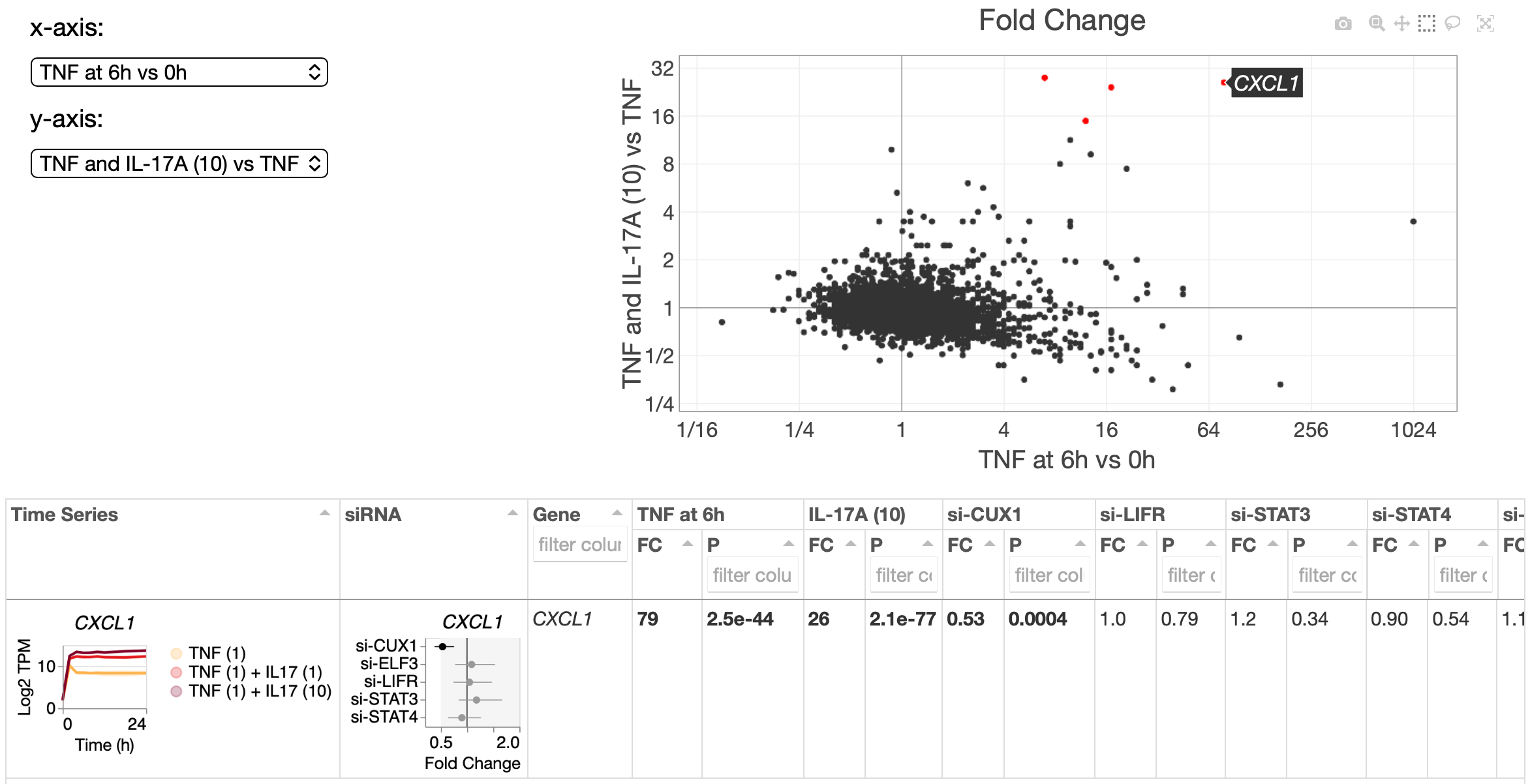
Gene Contrasts
Differential expression statistics for all genes across 8 time points, 3 conditions (TNF alone, TNF + IL-17A 1ng/mL, TNF + IL-17A 10ng/mL), and 5 siRNAs (anti-CUX1, anti-LIFR, anti-STAT3, anti-STAT4, anti-ELF3).
Launch Viewer →CUX1 and IκBζ (NFKBIZ) mediate the synergistic inflammatory response to TNF and IL-17A in stromal fibroblasts
PNAS (2020) · doi:10.1073/pnas.1912702117
Significance
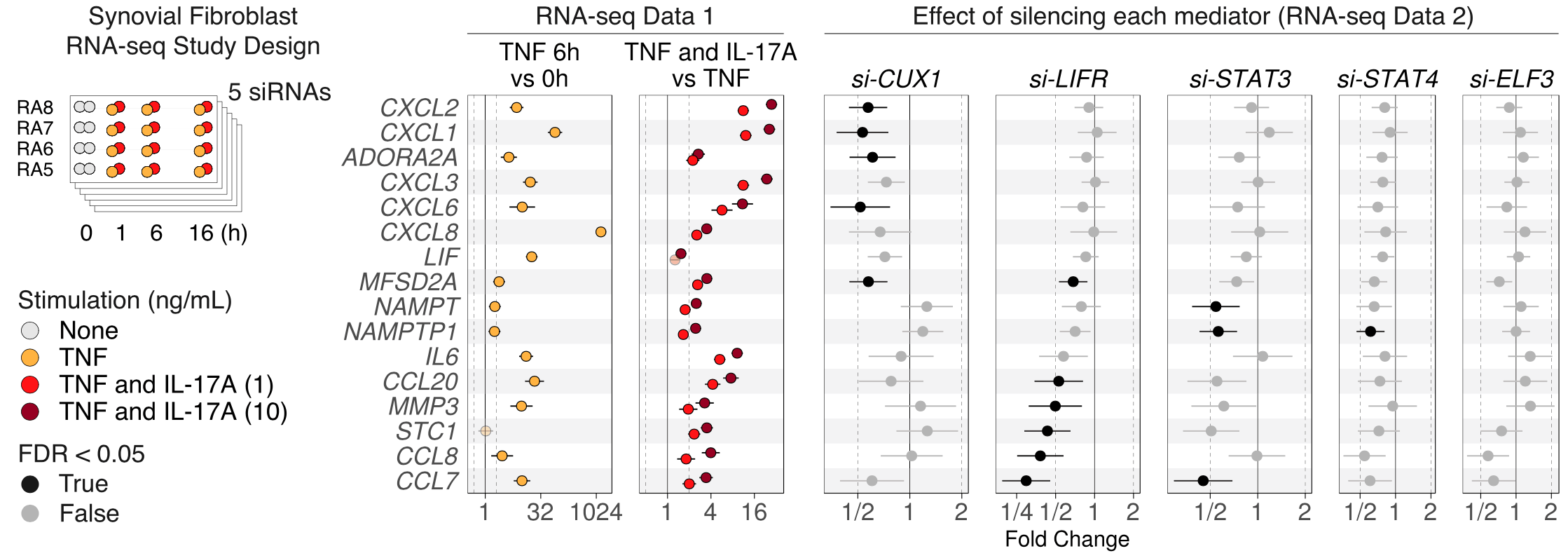
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by elevated levels of inflammatory cytokines including TNF and IL-17A. Synovial fibroblasts produce inflammatory factors such as IL-6 in response to TNF, and the addition of IL-17A synergistically amplifies this response. We profiled the transcriptomic response of synovial fibroblasts to TNF and different IL-17A dosages over time, and defined a set of genes induced by the addition of IL-17A. We found that CUX1 and IκBζ (NFKBIZ) mediate leukocyte recruitment by regulating production of multiple cytokines and chemokines. We show that gene targets of CUX1 are elevated in synovial tissue from individuals with rheumatoid arthritis relative to controls. While many studies have focused on leukocytes, our results highlight CUX1 and IκBζ as key regulators of inflammation in synovial fibroblasts.
Resources
Download Data
NCBI GEO: GSE129488
Source Code
Analysis: slowkow/fibrotime
Contact
Questions or comments? Get in touch.