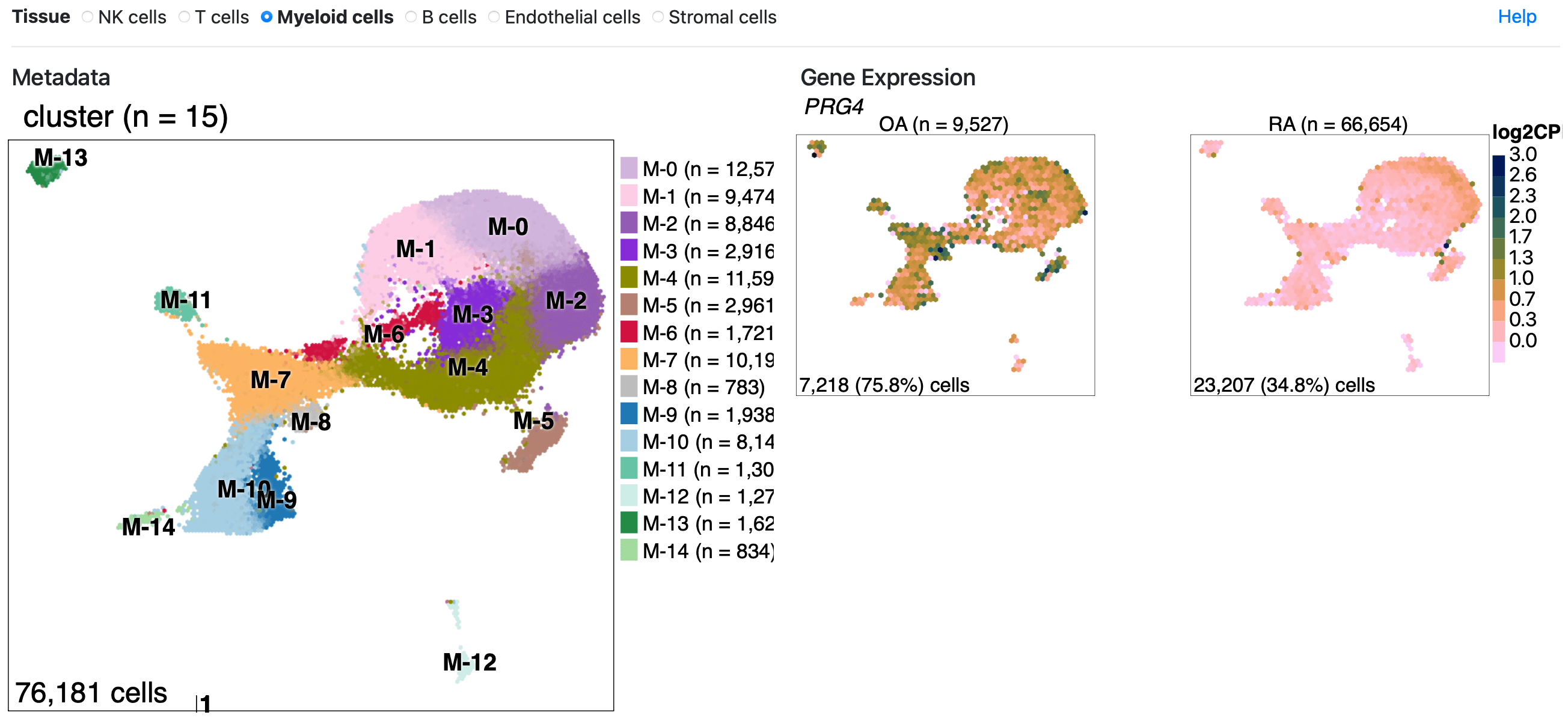
Cell Clusters
Metadata variables and gene expression in two-dimensional embeddings. Tissue: Stromal, Endothelial, Myeloid, T cell, NK cell, B cell.
Launch Viewer →Deconstruction of rheumatoid arthritis synovium defines inflammatory subtypes
Nature (2023) · doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06708-y
Abstract
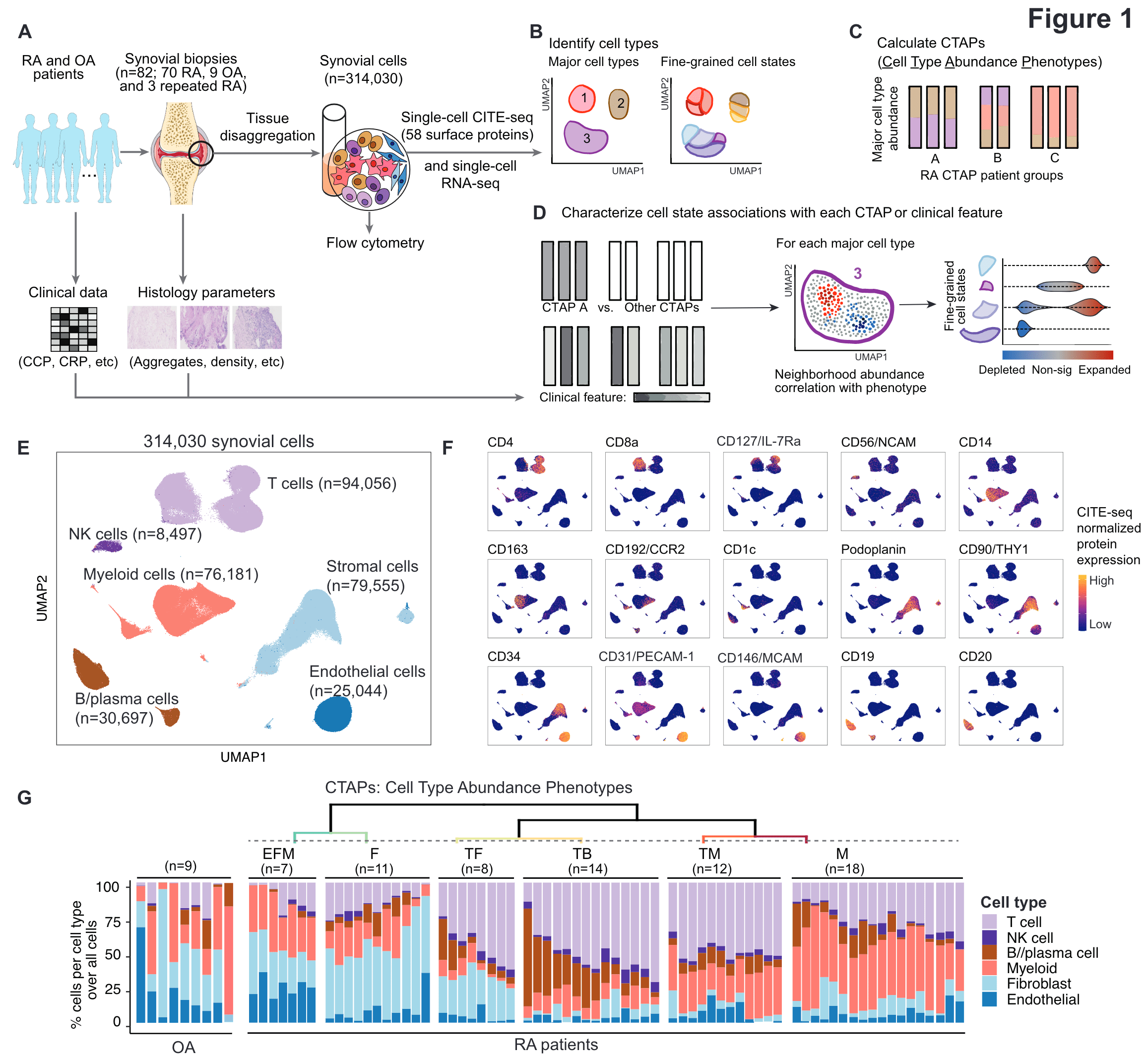
Rheumatoid arthritis is a prototypical autoimmune disease that causes joint inflammation and destruction. There is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, and the effectiveness of treatments varies across patients, suggesting an undefined pathogenic diversity. Here, to deconstruct the cell states and pathways that characterize this pathogenic heterogeneity, we profiled the full spectrum of cells in inflamed synovium from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. We used multi-modal single-cell RNA-sequencing and surface protein data coupled with histology of synovial tissue from 79 donors to build single-cell atlas of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue that includes more than 314,000 cells. We stratified tissues into six groups, referred to as cell-type abundance phenotypes (CTAPs), each characterized by selectively enriched cell states. These CTAPs demonstrate the diversity of synovial inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis, ranging from samples enriched for T and B cells to those largely lacking lymphocytes. Disease-relevant cell states, cytokines, risk genes, histology and serology metrics are associated with particular CTAPs. CTAPs are dynamic and can predict treatment response, highlighting the clinical utility of classifying rheumatoid arthritis synovial phenotypes. This comprehensive atlas and molecular, tissue-based stratification of rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue reveal new insights into rheumatoid arthritis pathology and heterogeneity that could inform novel targeted treatments.
Resources
Contact
Questions or comments? Get in touch with Fan Zhang.
Data from the laboratory of Dr. Soumya Raychaudhuri.